1. 初始化 React 项目
1. React 脚手架 create-react-app 初始化项目
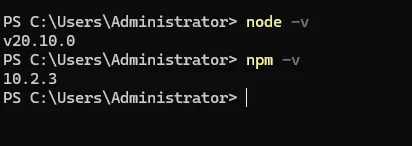
1. node 安装
下载地址:https://nodejs.org/en/download
版本选择:最新版带有LTS(稳定版)的。
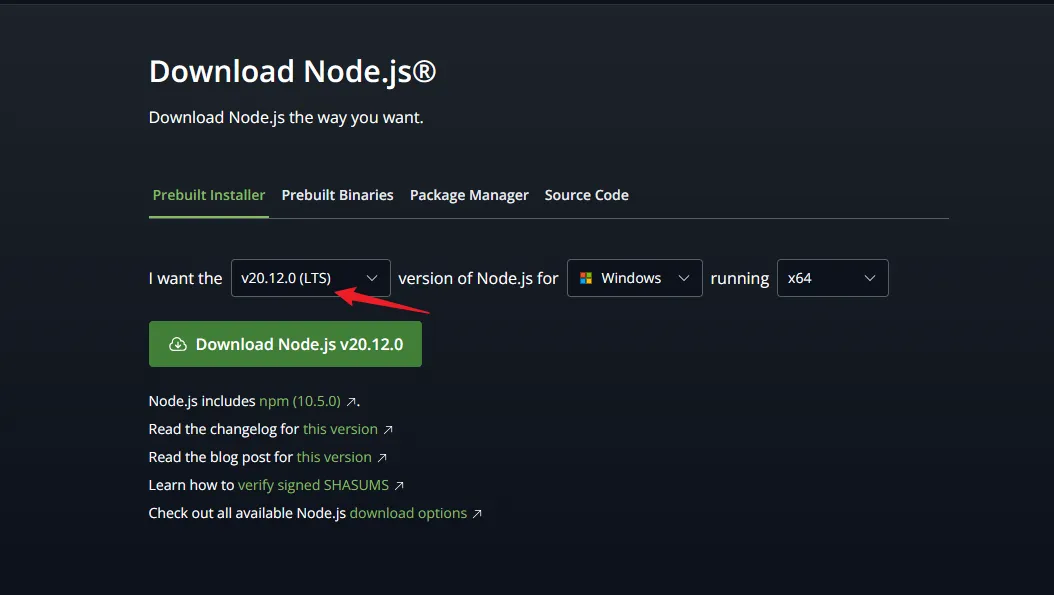
node下载好之后会自动带一个npm的包管理工具。
2. React脚手架 create-react-app
- 下载脚手架
npm 下载react脚手架
npm install create-react-app -g
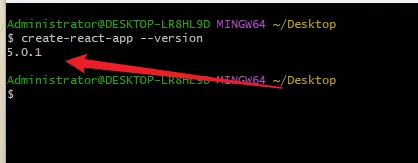
查看react脚手架版本
create-react-app --version
- 通过脚手架创建项目
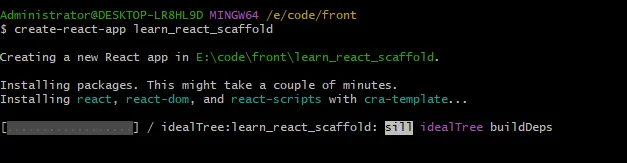
create-react-app 【项目名】,项目名不可以包含大写字母
这里创建过慢需要设置下淘宝源:
1
| npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
|
create-react-app learn_react_scaffold
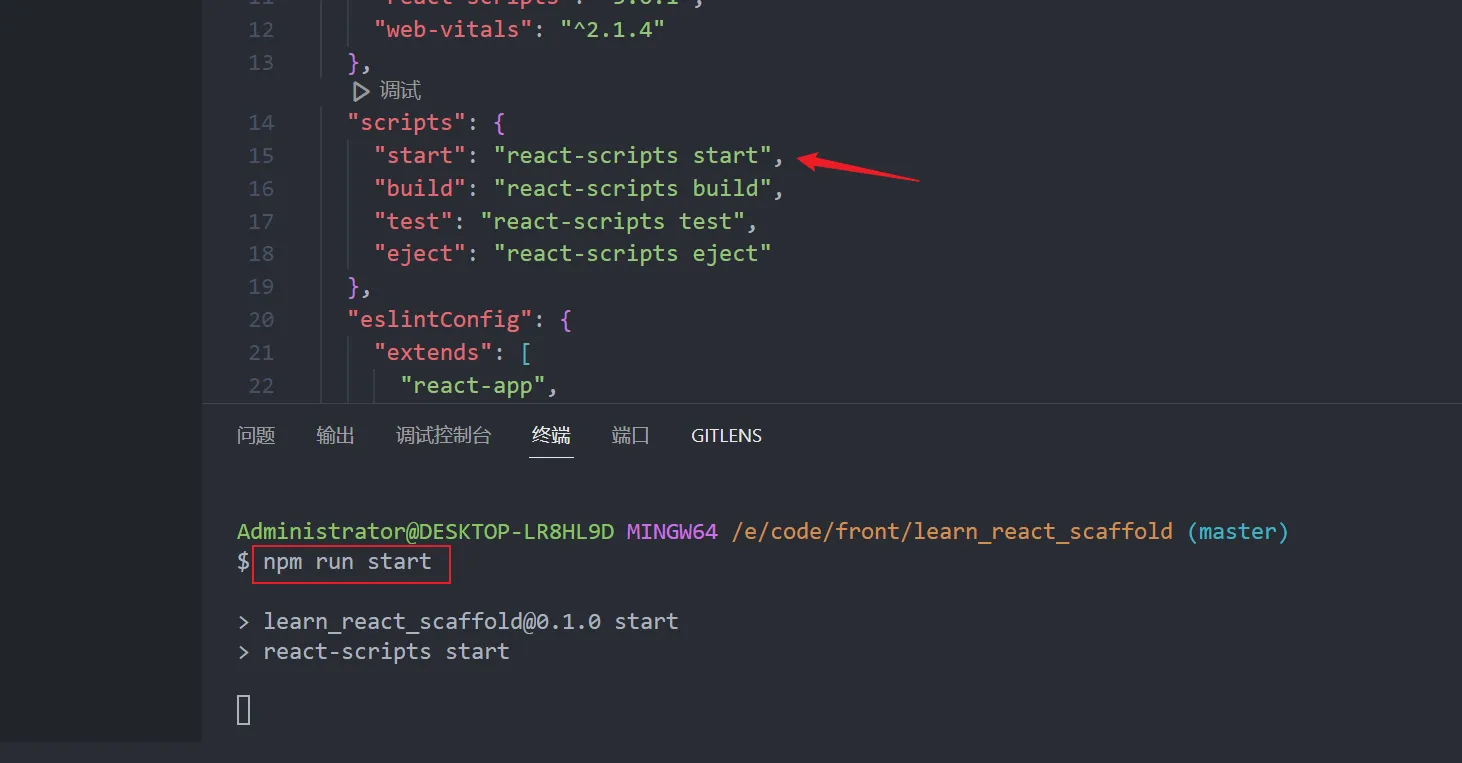
- 项目启动
通过运行npm run start运行项目。
react-scripts 命令集成了webpack的打包方式。
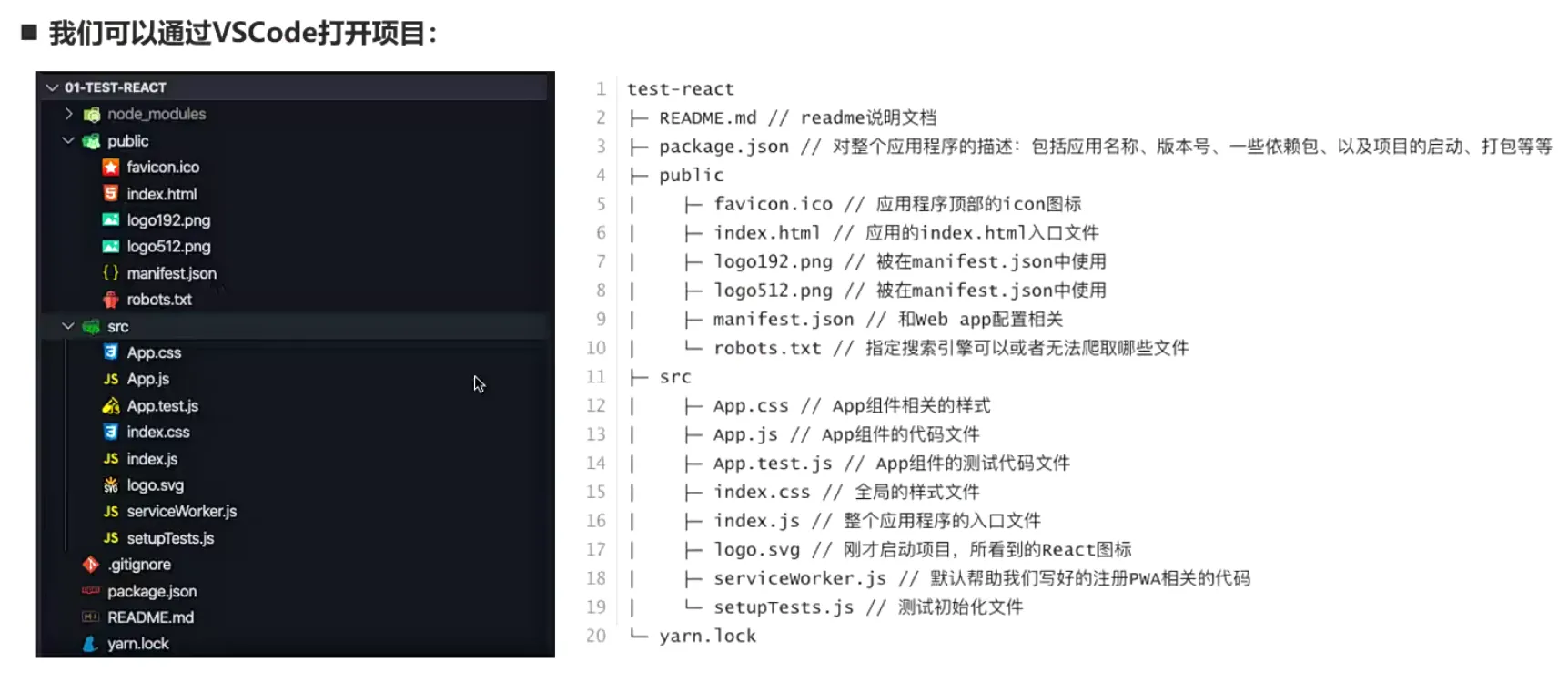
- 项目目录结构

2. 组件化开发
1. React组件划分
- 根据组件的定义方式,划分为函数组件和类组件。
- 根据组件内部是否有状体需要维护,划分为无状态组件和有状态组件。
- 根据组件的不同职责,划分为展示型组件和容器型组件。
- 函数组件,无状态组件和展示型组件主要关注ui展示。
- 类组件,有状态组件和容器型组件主要关注数据逻辑。
2. 类组件要求
- 组件的名称必须是大写字母开头。(无论是类组件还是函数式组件)
- 类组件需要继承自 React.Component。
- 类组件必须实现 render 函数。
3. Helloworld(类组件的封装细节)
1. install
1
2
3
4
5
| # 切换至淘宝源
npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com
# 使用 create-react-app 创建 react 项目
npx create-react-app 03-react-component
|
2. 项目结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import ReactDom from "react-dom/client"
import App from "./App"
const root = ReactDom.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"))
root.render(<App />)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import react from "react"
import HelloWorld from "./components/HelloWorld"
class App extends react.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>React App</h1>
<HelloWorld />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import react from "react"
class HelloWorld extends react.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: "hello world"
}
}
render() {
const { message } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h2>{message}</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
export default HelloWorld
|
3. react-scripts 命令对应的 webpack 配置
webpack配置默认隐藏:
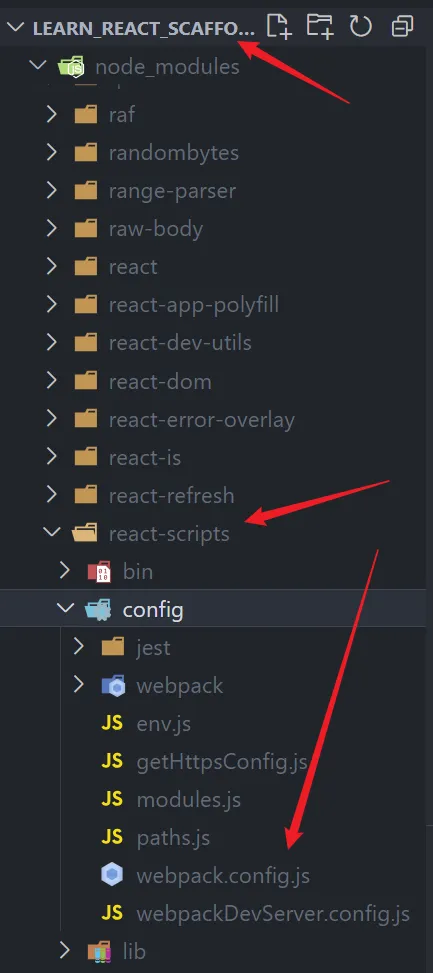
执行
弹出webpack配置
文件变动:
4. render 函数的返回值

4. 函数式组件的封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| export default function App() {
return (
<div>
<h1>React functional App</h1>
</div>
)
}
|
5. 类组件的生命周期
参考:Component – React 中文文档

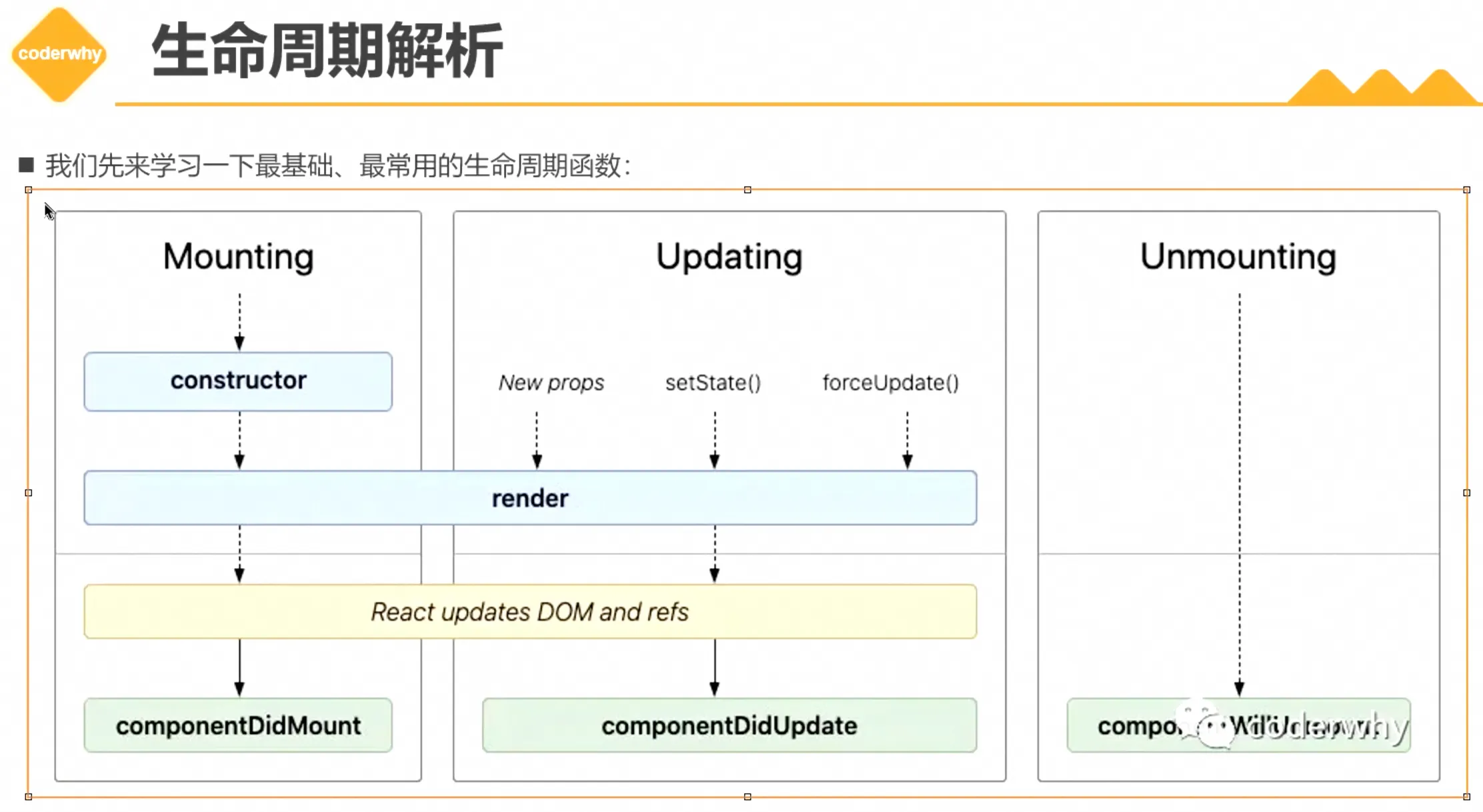
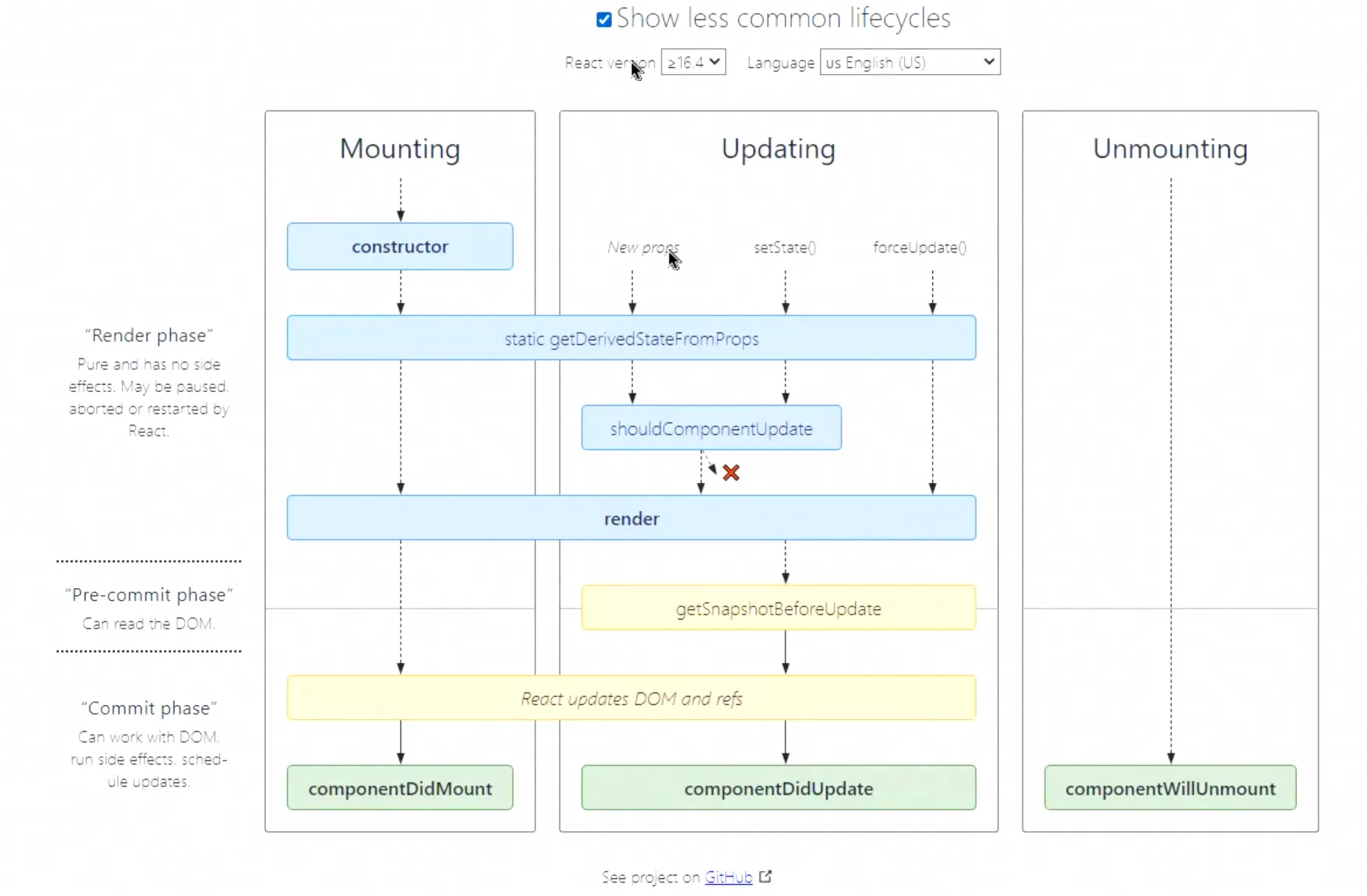
1. 常用的生命周期代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import React from "react"
import HelloWorld from "./HelloWorld"
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
isShowHW: true
}
}
switchHWShow() {
this.setState({
isShowHW: !this.state.isShowHW
})
}
render() {
const { isShowHW } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h1>React App</h1>
<button onClick={e => this.switchHWShow()}>切换</button>
{ isShowHW && <HelloWorld />}
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| import React from "react";
class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
constructor() {
console.log("hello world constructor ~")
super()
this.state = {
message: "hello world"
}
}
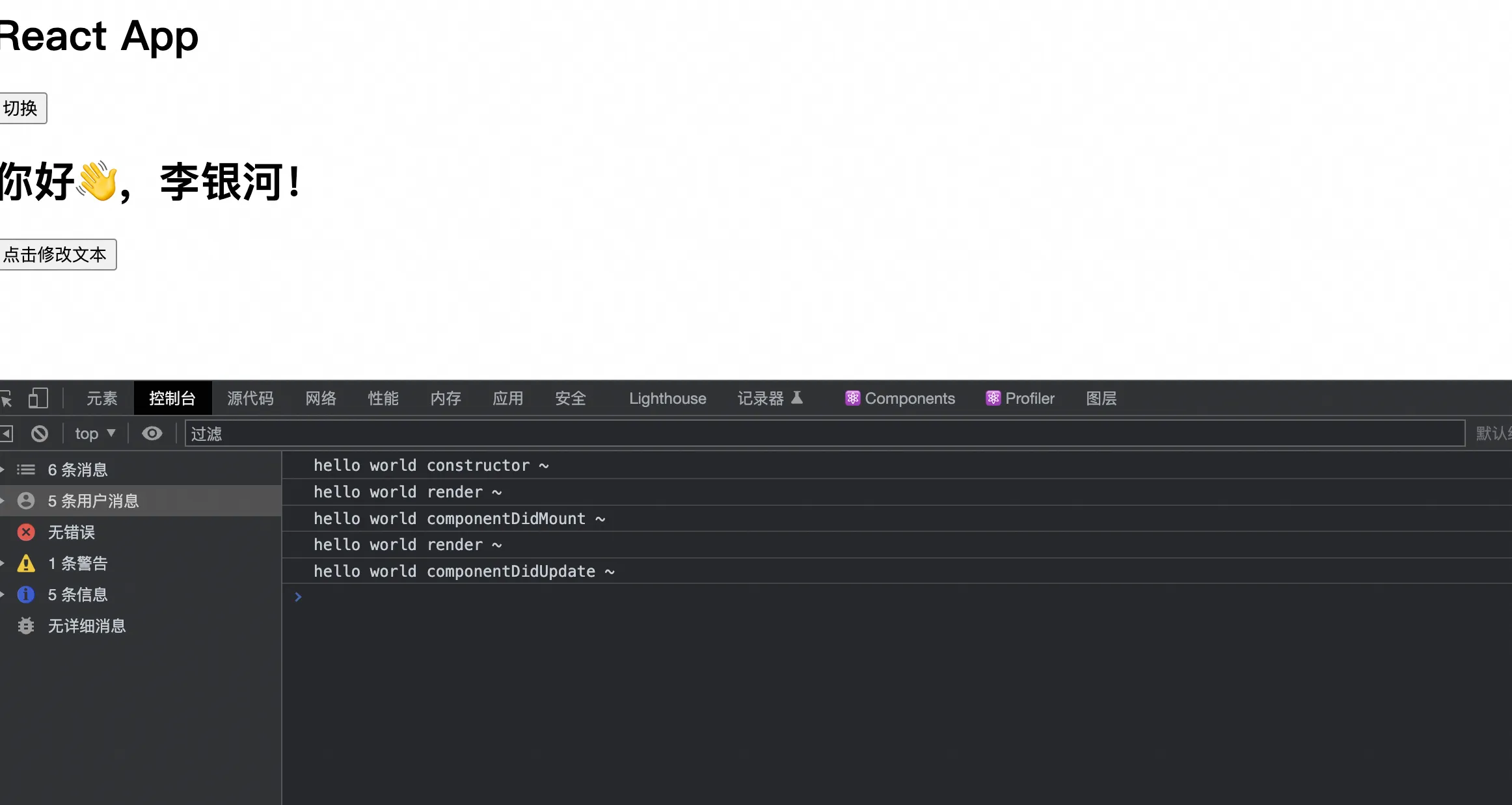
changeText() {
this.setState({
message: "你好👋,李银河!"
})
}
render() {
console.log("hello world render ~")
const { message } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h1>{ message }</h1>
<button onClick={ e => this.changeText() }>点击修改文本</button>
</div>
)
}
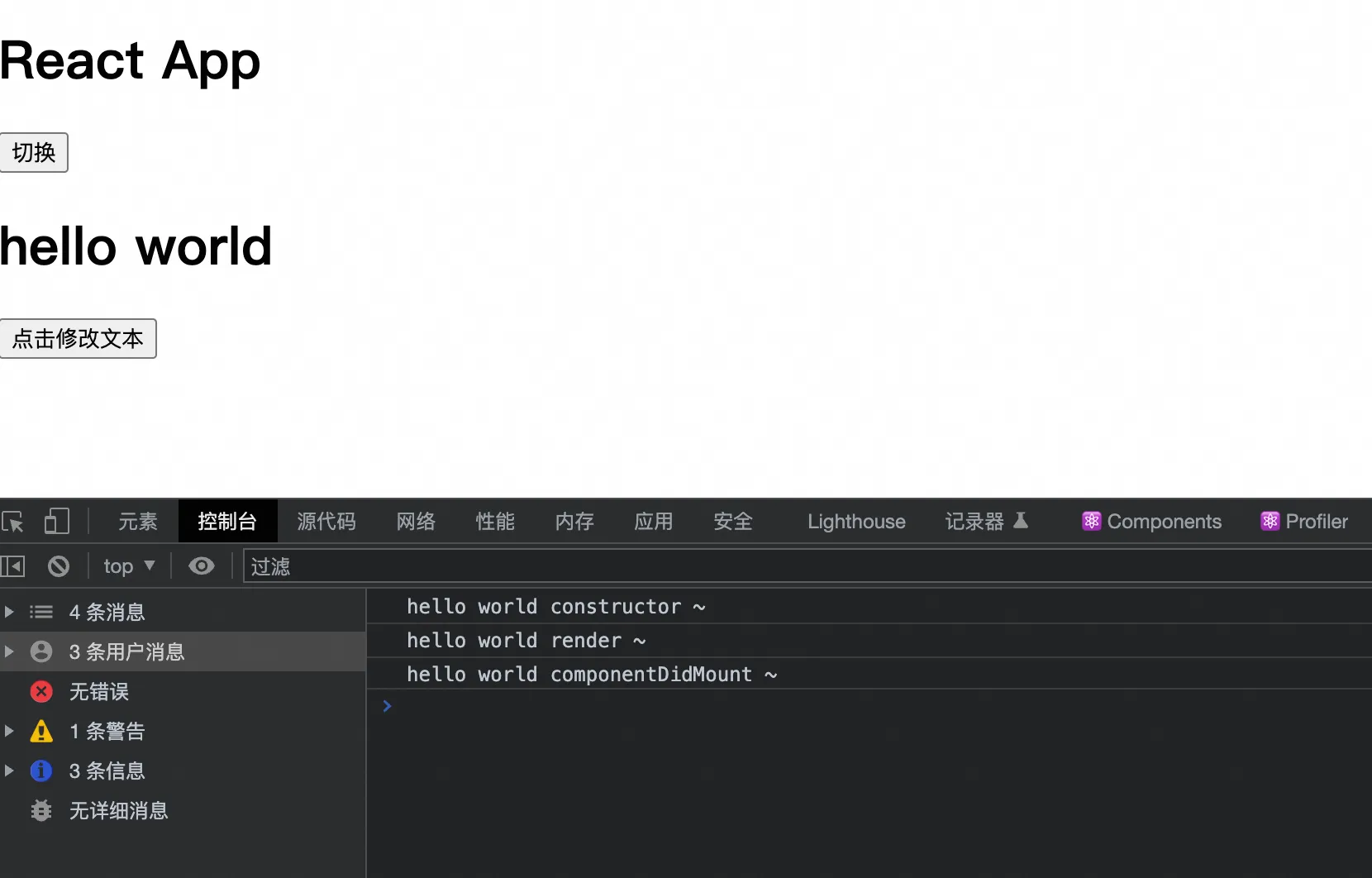
componentDidMount() {
console.log("hello world componentDidMount ~")
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log("hello world componentDidUpdate: ", prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
}
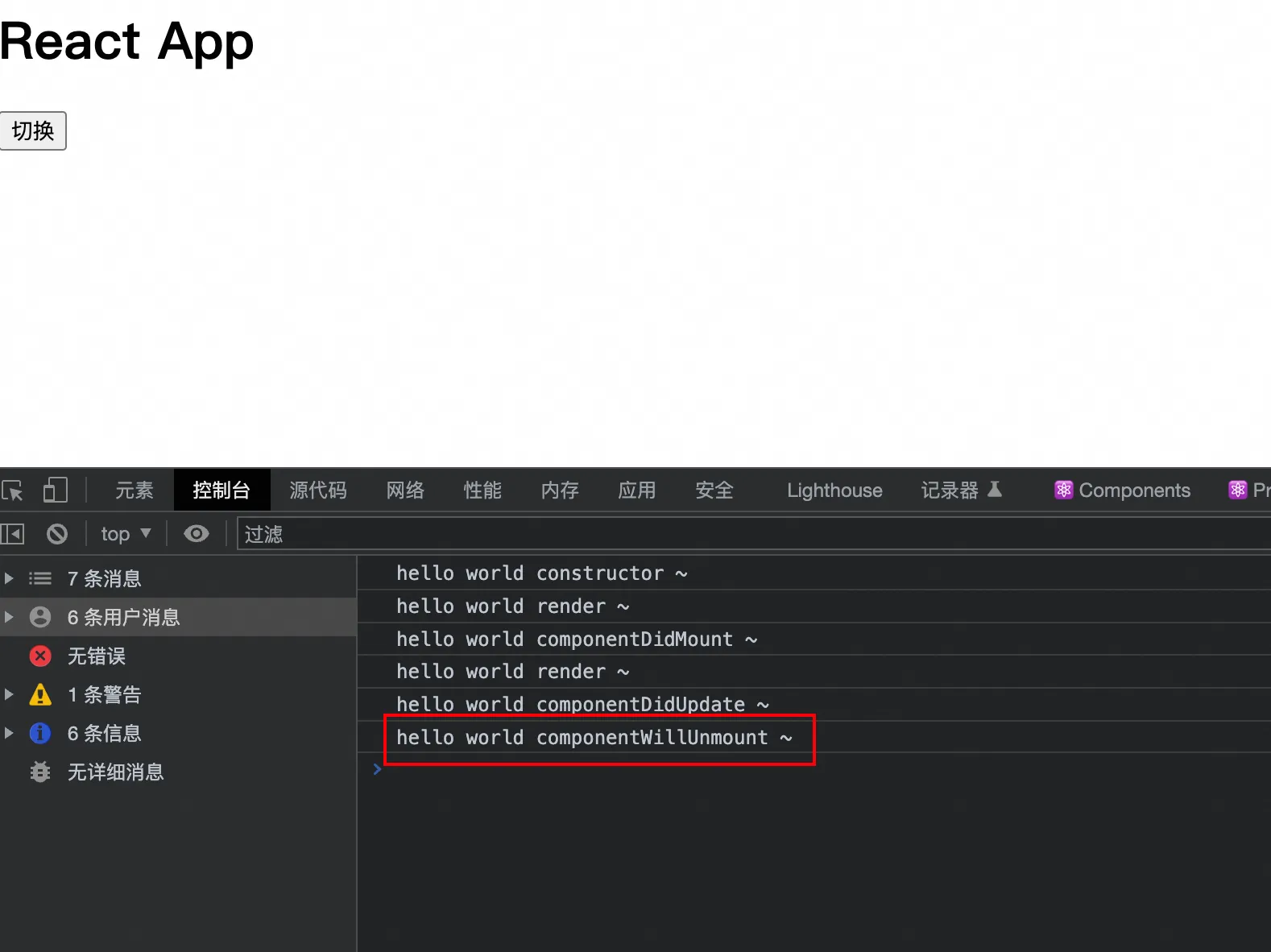
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log("hello world componentWillUnmount ~")
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log("hello world shouldComponentUpdate ~")
return true
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() {
console.log("hello world getSnapshotBeforeUpdate ~")
return {
scrollPosition: 1000,
prevMessage: this.state.message
}
}
}
export default HelloWorld
|
初次页面:
点击修改文本:
点击切换:
2. 常用的生命周期详解


3. 不常用的生命周期函数
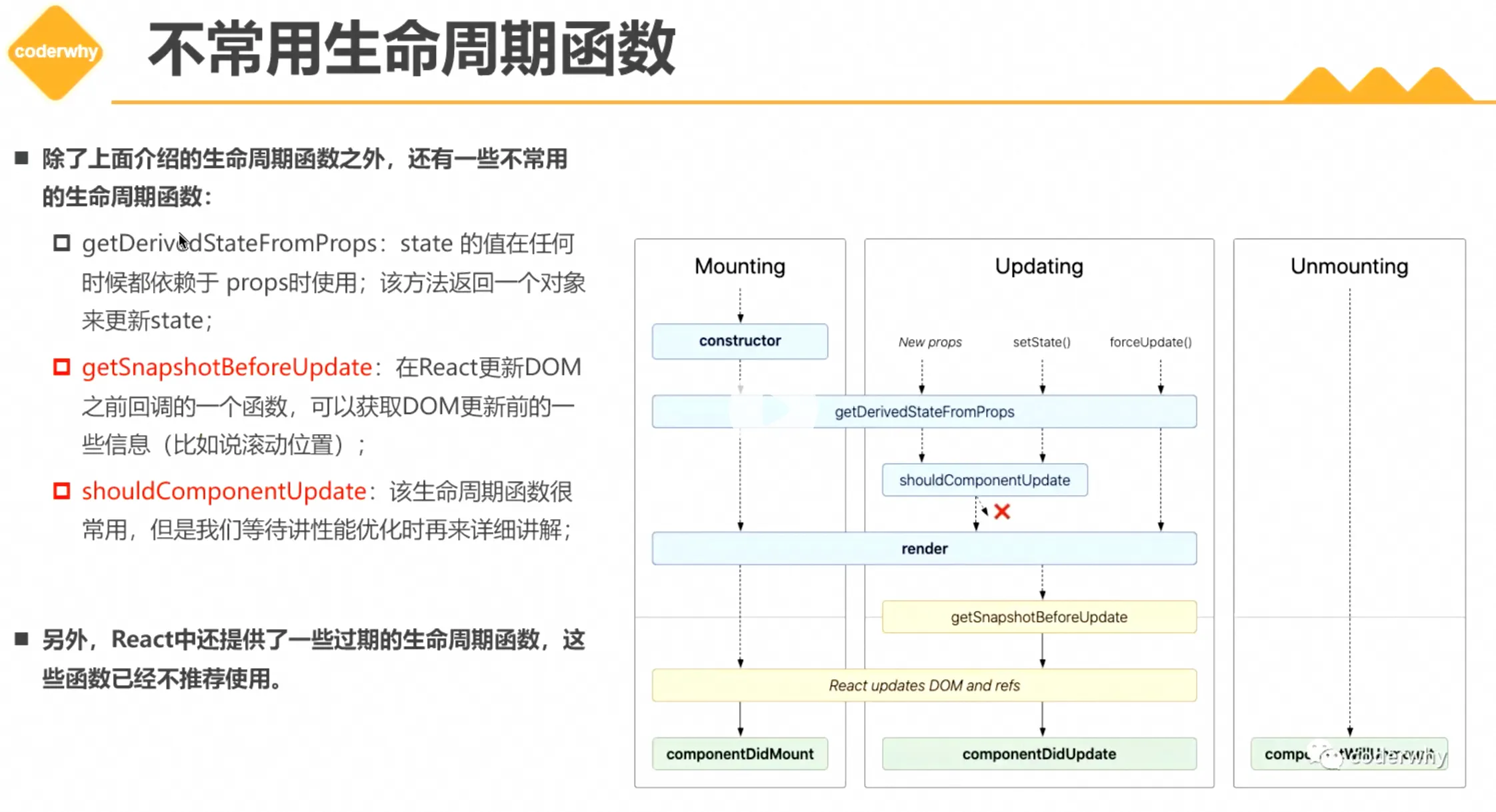
6. 组件通信
1. 父传子
2. 父传子代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Father from './c-cpns/Father'
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Father />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Children from './Children'
class Father extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
title: '父组件',
message: '我是父组件的数据'
}
}
render() {
const { message, title } = this.state
return (
<div>
<p>我是父组件</p>
<Children message={message} title={title} />
</div>
)
}
}
export default Father
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
class Children extends Component {
constructor(props) {
console.log(props)
super(props)
}
render() {
const { message, title } = this.props
return (
<div>
<span>我是子组件</span>
<br/>
<span>父组件中的tilte:{title}</span>
<br/>
<span>父组件中的message:{message}</span>
</div>
)
}
}
export default Children
|
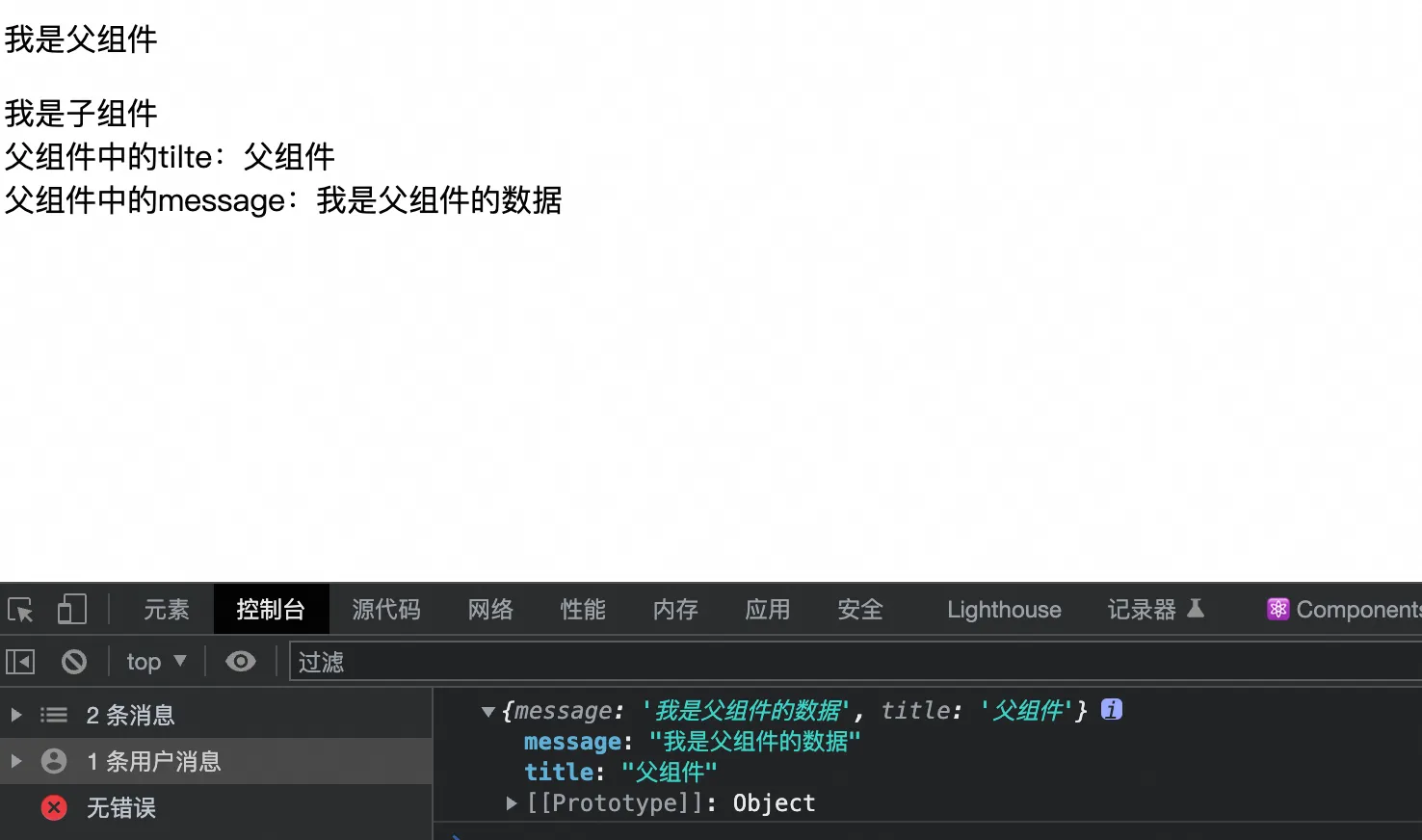
效果:
3. 类型校验
参考:使用 PropTypes 进行类型检查 – React (reactjs.org)
4. 子传父
• 通过从父组件中传递过来的函数将参数传递进去实现通信
子传父代码示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import AddCounter from './AddCounter'
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
counter: 100
}
}
render() {
const { counter } = this.state
return (
<div>
counter: { counter }
<AddCounter addCounter={(number)=> this.setState({ counter: counter + number })} />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
class AddCounter extends Component {
addCounter(count) {
this.props.addCounter(count)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => this.addCounter(1)}>+1</button>
<button onClick={() => this.addCounter(5)}>+5</button>
<button onClick={() => this.addCounter(10)}>+10</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default AddCounter
|
7. 组件的插槽实现
7.1. 实现方式一(不推荐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import NavBar from './nav-bar'
export class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<NavBar>
<span>插槽1</span>
<span>插槽2</span>
<span>插槽3</span>
</NavBar>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
export class NavBar extends Component {
render() {
const { children } = this.props
return (
<div>
<h2>1. 可以通过数组的形式取得子组件</h2>
<span>{children[0]}</span>
<br />
<span>{children[1]}</span>
<br />
<span>{children[2]}</span>
<h2>2. 可以通过遍历的形式取得子组件</h2>
{React.Children.map(children, (child, index) => {
return (
<div key={index}>{child}</div>
)
})}
<h2>3. 直接获取 children</h2>
<span>{children}</span>
</div>
)
}
}
NavBar.propTypes = {
children: PropTypes.array,
}
export default NavBar
|
2. 实现方式二(推荐)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import NavBarTwo from './nav-bar-two'
export class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<NavBarTwo firstSlot={<div>我是插槽1</div>} secondSlot={<div>我是插槽2</div>} thirdSlot={<div>我是插槽3</div>} />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class NavBarTwo extends Component {
render() {
const { firstSlot, secondSlot, thirdSlot } = this.props
return (
<div>
<div>{firstSlot}</div>
<div>{secondSlot}</div>
<div>{thirdSlot}</div>
</div>
)
}
}
export default NavBarTwo
|
3. 作用域插槽
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import NavBar from './nav-bar'
export class App extends Component {
selectChange(item) {
console.log(item)
switch (item) {
case 'home':
return <div style={{color: 'red'}}>首页</div>
case 'about':
return <div style={{color: 'skyblue'}}>关于</div>
case 'contact':
return <div style={{color: 'black'}}>联系我们</div>
default:
return <div>首页</div>
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<NavBar slot={item => this.selectChange(item)} />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class NavBar extends Component {
render() {
const { slot } = this.props
return (
<div>{slot("about")}</div>
)
}
}
export default NavBar
|
8. 非父子组件通信 - Context
1. 作用
• 非父子组件间的数据共享



2. 类组件中使用 Context
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import { createContext } from "react";
const ThemeContext = createContext()
export default ThemeContext
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
import Home from './Home'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
info: { color: 'red', level: '高级' }
}
}
render() {
const { info } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
// 2. 在context中存值
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{color: "red", size: "30"}}>
<Home {...info}></Home>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
export class Home extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
title: '我是Home组件'
}
}
render() {
console.log(this.context)
const { title } = this.state
const {color, size} = this.context
return (
<div>
{ title }
<span>下面是 ThemeContext 中的数据:</span>
{/* 第一种写法: */}
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{
(ctx) => {
return (
<div>
<span>color: { ctx.color }</span>
<br/>
<span>size: { ctx.size }</span>
</div>
)
}
}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
{/* 第二种写法: */}
<div>
<span>第二种写法:</span>
<br/>
<span>color: {color}</span>
<br/>
<span>size: {size}</span>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
Home.contextType = ThemeContext
export default Home
|

3. 函数式组件获取 context 中的数据

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
import Home from './Home'
import HomeBanner from './HomeBanner'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
info: { color: 'red', level: '高级' }
}
}
render() {
const { info } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{color: "red", size: "30"}}>
<Home {...info}></Home>
<HomeBanner/>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import React from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
const HomeBanner = () => {
return (
<>
<div>HomeBanner 函数式组件</div>
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{
(ctx) => {
return (
<div>
<span>color: { ctx.color }</span>
<br/>
<span>size: { ctx.size }</span>
</div>
)
}
}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
</>
)
}
export default HomeBanner
|

4. context 中的默认值设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import { createContext } from "react";
const ThemeContext = createContext({nickname: 'coderwhy', level: '高级'})
export default ThemeContext
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
export class Profile extends Component {
render() {
return (
<>
<div>Profile</div>
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{
(ctx) => {
return (
<div>
<span>nickname: { ctx.nickname }</span>
<br/>
<span>level: { ctx.level }</span>
</div>
)
}
}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
</>
)
}
}
export default Profile
|

5. 多个 context 使用
1
2
3
4
5
| import { createContext } from "react";
const UserContext = createContext()
export default UserContext
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
import Home from './Home'
import HomeBanner from './HomeBanner'
import Profile from './Profile'
import UserContext from './context/user-context'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
info: { color: 'red', level: '高级' }
}
}
render() {
const { info } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
<ThemeContext.Provider value={{color: "red", size: "30"}}>
// 这里多个context嵌套使用
<UserContext.Provider value={{name: "wuyanzu", age: "18"}}>
<Home {...info}></Home>
<HomeBanner/>
</UserContext.Provider>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
<Profile></Profile>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import ThemeContext from './context/theme-context'
import UserContext from './context/user-context'
export class Home extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
title: '我是Home组件'
}
}
render() {
console.log(this.context)
const { title } = this.state
const {color, size} = this.context
return (
<div>
{ title }
<span>下面是 ThemeContext 中的数据:</span>
{/* 第一种写法: */}
<ThemeContext.Consumer>
{
(ctx) => {
return (
<div>
<span>color: { ctx.color }</span>
<br/>
<span>size: { ctx.size }</span>
</div>
)
}
}
</ThemeContext.Consumer>
<UserContext.Consumer>
{
(ctx) => {
return (
<div>
<span>name: { ctx.name }</span>
<br/>
<span>age: { ctx.age }</span>
</div>
)
}
}
</UserContext.Consumer>
{/* 第二种写法: */}
<div>
<span>第二种写法:</span>
<br/>
<span>color: {color}</span>
<br/>
<span>size: {size}</span>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
Home.contextType = ThemeContext
export default Home
|

9. 非父子组件通信 - 事件总线
1. Install
1
| npm install hy-event-store
|
2. demo case
- 创建 eventBus 对象
1
2
3
4
5
| import { HYEventBus } from 'hy-event-store'
const eventBus = new HYEventBus()
export default eventBus
|
- 使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import eventBus from './utils/event-bus'
import HelloOne from './component/HelloOne'
import HelloTwo from './component/HelloTwo'
export class App extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
eventBus.on("helloOneSendEvent", (event) => {
console.log('我是App组件,监听到了来自HelloOne组件的事件')
console.log(event)
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
eventBus.off("helloOneSendEvent", () => {})
}
render() {
return (
<>
<h1>App</h1>
<HelloOne/>
<HelloTwo/>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import eventBus from '../utils/event-bus'
export class HelloOne extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
event: '我是来自HelloOne组件的一个事件'
}
}
eventSend = () => {
eventBus.emit('helloOneSendEvent', this.state.event)
}
render() {
return (
<>
<h2>HelloOne</h2>
<button onClick={this.eventSend}>click</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default HelloOne
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import eventBus from '../utils/event-bus'
export class HelloTwo extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
eventBus.on("helloOneSendEvent", (event) => {
console.log('我是HelloTwo组件,监听到了来自HelloOne组件的事件')
console.log(event)
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
eventBus.off("helloOneSendEvent", () => {})
}
render() {
return (
<h2>HelloTwo</h2>
)
}
}
export default HelloTwo
|
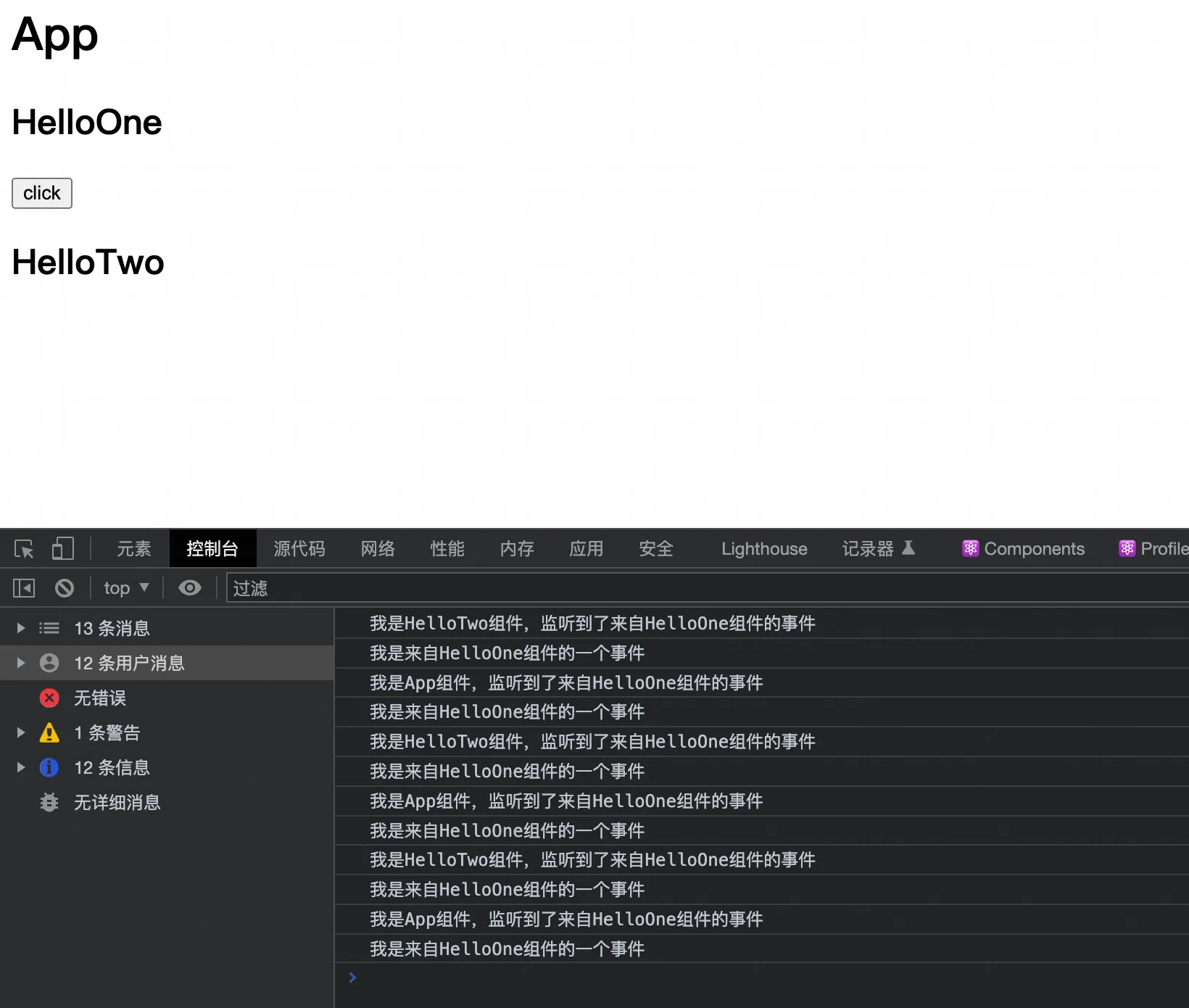
3. 存在this绑定问题
1. 问题复现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import eventBus from '../utils/event-bus'
export class HelloTwo extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
eventBus.on("helloOneSendEvent", this.handleHelloOneEvent)
}
handleHelloOneEvent(event) {
console.log('我是HelloTwo组件,监听到了来自HelloOne组件的事件')
console.log(event)
console.log(this)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
eventBus.off("helloOneSendEvent", () => {})
}
render() {
return (
<h2>HelloTwo</h2>
)
}
}
export default HelloTwo
|
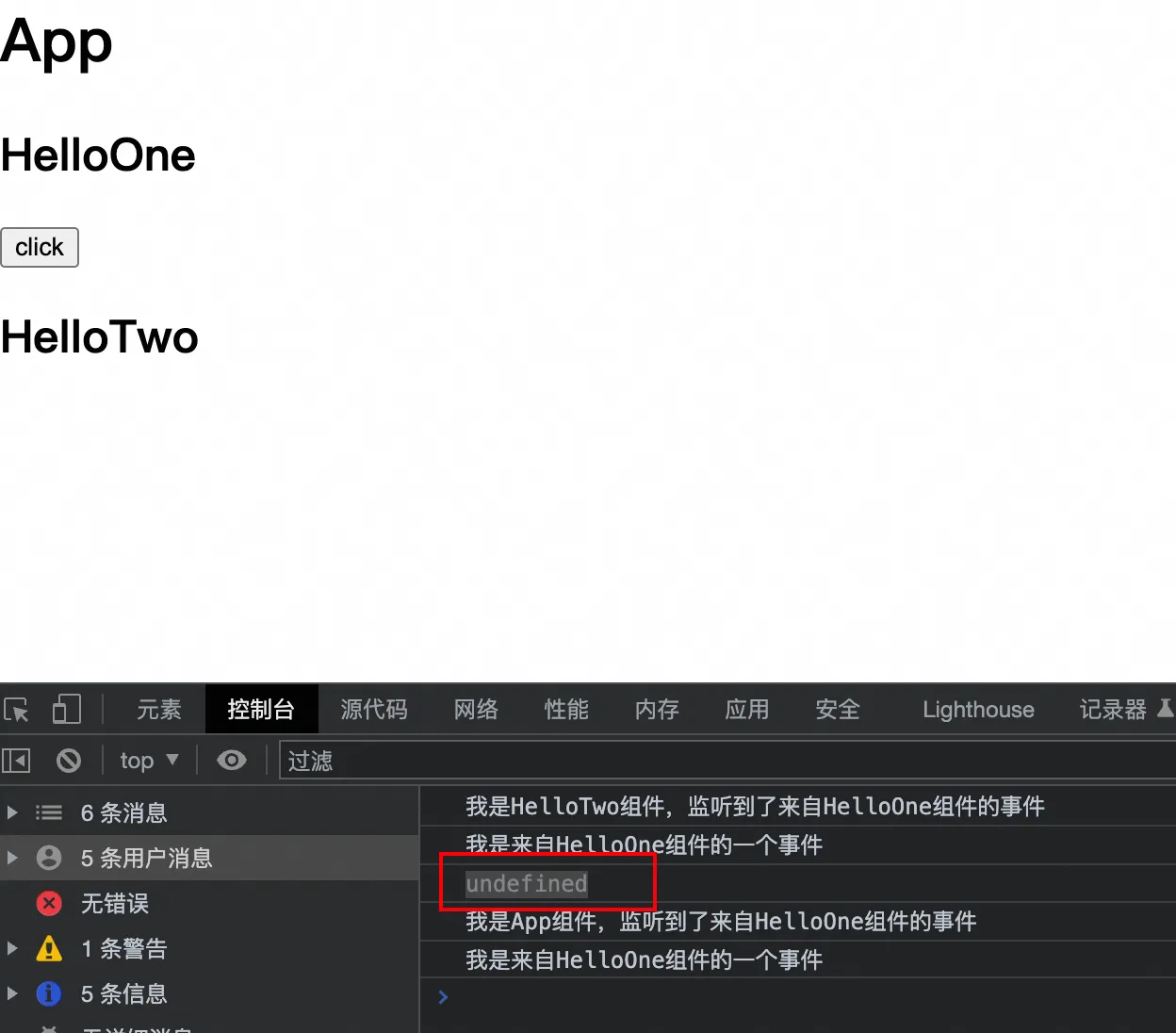
2. 修复
方法一和方法二任选一个就可以:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import eventBus from '../utils/event-bus'
export class HelloTwo extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
eventBus.on("helloOneSendEvent", this.handleHelloOneEvent)
}
handleHelloOneEvent = (event) => {
console.log('我是HelloTwo组件,监听到了来自HelloOne组件的事件')
console.log(event)
console.log(this)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
eventBus.off("helloOneSendEvent", () => {})
}
render() {
return (
<h2>HelloTwo</h2>
)
}
}
export default HelloTwo
|
10. setState 用法及原理参考
React(四) 事件总线,setState的原理,PureComponent优化React性能,ref获取类组件与函数组件_react事件总线-CSDN博客
1. setState的三种用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: "Hello React"
}
}
changeMsg() {
this.setState({
message: "你好啊,李银河!"
})
}
render() {
const { message } = this.state
return (
<>
<h2>{message}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.changeMsg()}>点击我</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import ReactDom from "react-dom/client"
import App from "./10_setState的三种用法/App"
const root = ReactDom.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"))
root.render(<App />)
|
好处一: 可以在回调函数中编写对新state处理的逻辑
好处二: 当前的回调函数会将之前的state和props传递进来
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: "Hello React"
}
}
changeMsg() {
this.setState((state, props) => {
console.log(state.message, props)
return {
message: "你好啊,李银河!"
}
})
}
render() {
const { message } = this.state
return (
<>
<h2>{message}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.changeMsg()}>点击我</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
- 用法三:setState 是一个异步调用,传入 callback 来使用最新的 state 的值处理逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: "Hello React"
}
}
changeMsg() {
this.setState({ message: "你好啊,李银河!"}, () => {
console.log(this.state.message)
})
}
render() {
const { message } = this.state
return (
<>
<h2>{message}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.changeMsg()}>点击我</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
2. react 为什么设计成异步的?
https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/11527

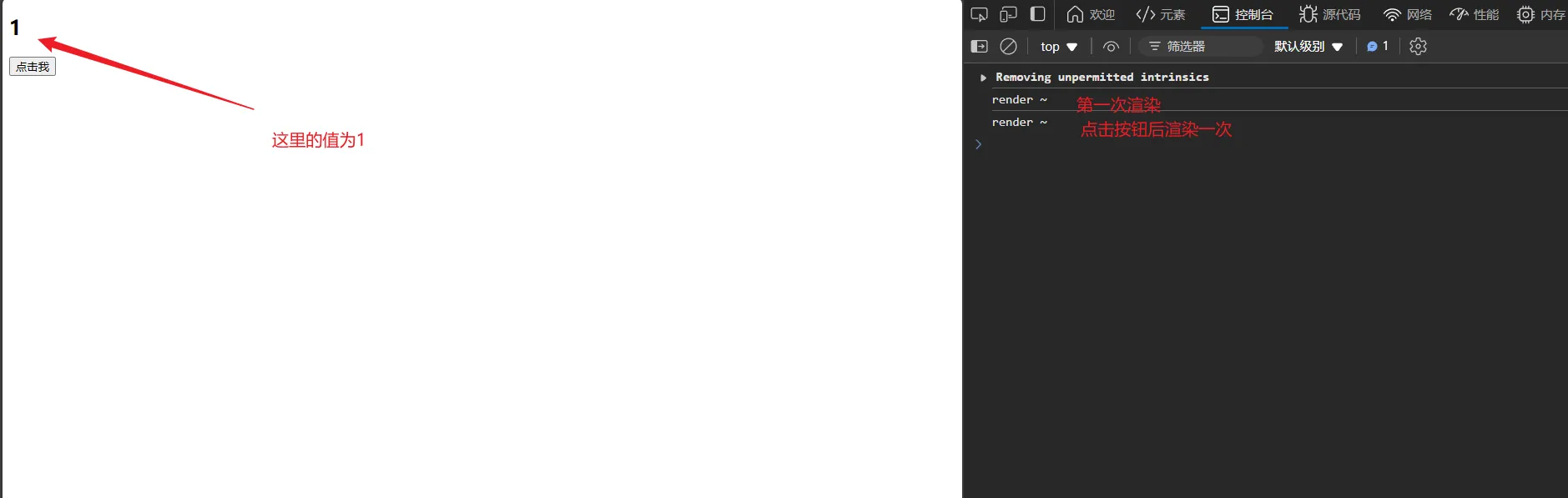
📌 注意事项一:setState是批量更新的,不是每次调用都会更新
• 错误使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
counter: 0
}
}
increament() {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
}
render() {
console.log("render ~")
const { counter } = this.state
return (
<>
<h2>{counter}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.increament()}>点击我</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
• 我们要想每次都拿到最新的 state 的值使用,应该用回调函数的方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
counter: 0
}
}
increment() {
this.setState((state) => {
return {
counter: state.counter + 1
}
})
this.setState((state) => {
return {
counter: state.counter + 1
}
})
this.setState((state) => {
return {
counter: state.counter + 1
}
})
}
render() {
console.log("render ~")
const { counter } = this.state
return (
<>
<h2>{counter}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>点击我</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|

📌 注意事项二:setState 在 React 18 之前是同步的,React 18 之后是异步的
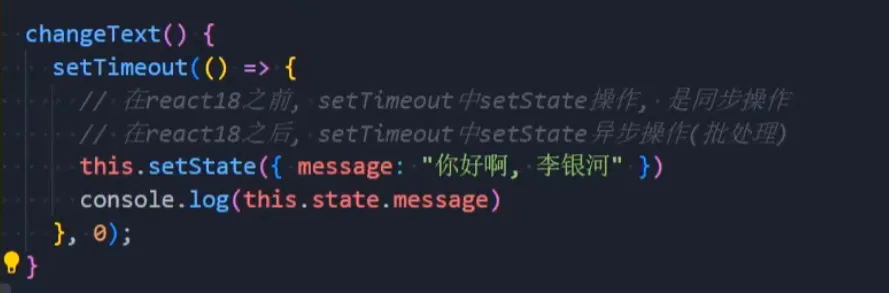
💡 将setState异步变为同步
- 使用callback回调参数
- 使用react-dom中的flushSync
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import { flushSync } from 'react-dom'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
counter: 0
}
}
increment() {
flushSync(() => {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
})
console.log(this.state.counter)
}
render() {
console.log("render ~")
const { counter } = this.state
return (
<>
<h2>{counter}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>点击我</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
11. React 性能优化
1. diff 算法和 key 的作用
https://juejin.cn/post/6967626390380216334


2. render 函数优化
- 问题
问题说明:在每个组件中包含的子组件,只要父组件的一个 state 或者 props 值被修改,该组件以及子组件都会重新执行 render 函数
👨🏻💻 code demo:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Home from './Home'
import Recommend from './Recommend'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
msg: "Hello React",
counter: 0
}
}
changeMsg() {
this.setState({
msg: "你好啊,李银河!"
})
}
increment() {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
}
render() {
console.log("App render ~")
const { msg, counter } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
<h2>{msg} - {counter}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.changeMsg()}>修改msg</button>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button>
<Home />
<Recommend />
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class Home extends Component {
render() {
console.log("Home render ~")
return (
<div>Home</div>
)
}
}
export default Home
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class Recommend extends Component {
render() {
console.log("Recommend render ~")
return (
<div>Recommend</div>
)
}
}
export default Recommend
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import ReactDom from "react-dom/client"
import App from "./11_render函数的优化/App"
const root = ReactDom.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"))
root.render(<App />)
|

💡 解法一:使用 shouldComponentUpdate 来阻止更新(SCU优化)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
export class Home extends Component {
shouldComponentUpdate() {
return false
}
render() {
console.log("Home render ~")
return (
<div>Home</div>
)
}
}
export default Home
|
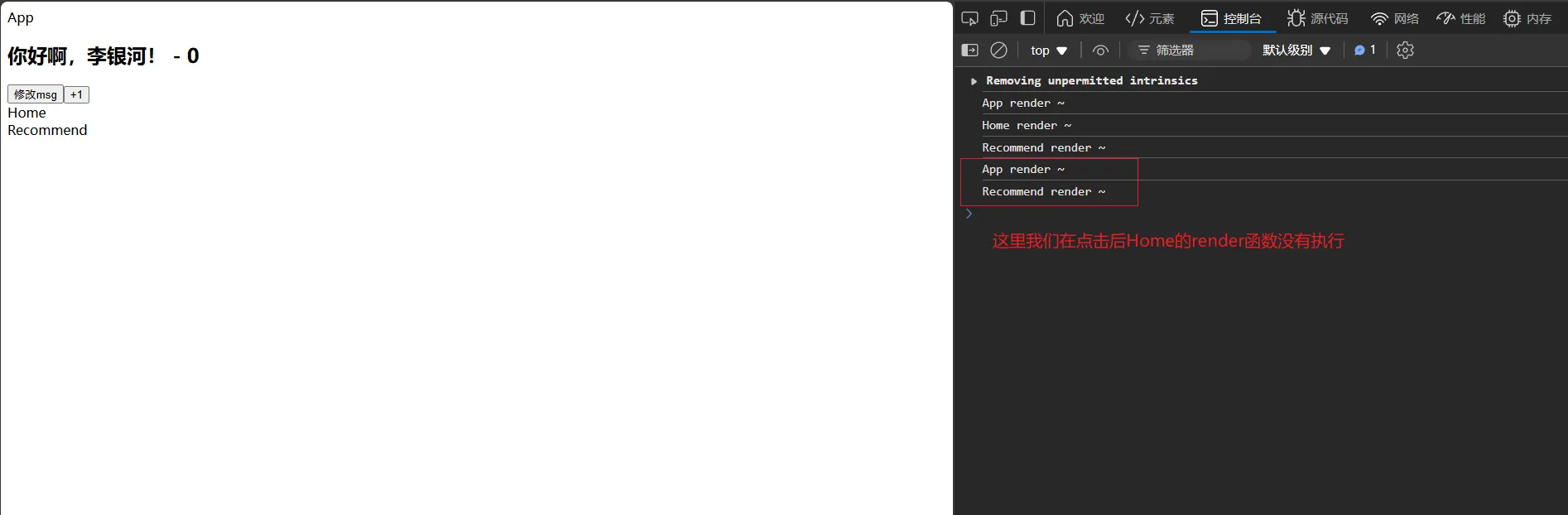
• 同样,当我们的 state 的值没有被修改时,也可以这样来优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| import React, { Component } from 'react'
import Home from './Home'
import Recommend from './Recommend'
export class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
msg: "Hello React",
counter: 0
}
}
changeMsg() {
this.setState({
msg: "Hello React"
})
}
increment() {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (this.state === nextState) {
return true
}
return false
}
render() {
console.log("App render ~")
const { msg, counter } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
<h2>{msg} - {counter}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.changeMsg()}>修改msg</button>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button>
<Home />
<Recommend />
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|

💡 解法二:(推荐)使用 PureComponent 和 memo 来进行 render 优化
- 类组件继承 PureComponent, 函数式组件用memo包裹,目的还是当 state 或者 props 的值不发生变化时不进行 render 渲染
👨🏻💻 code demo:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
import Home from './Home'
import Recommend from './Recommend'
import Profile from './Profile'
export class App extends PureComponent {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
msg: "Hello React",
counter: 0
}
}
changeMsg() {
this.setState({
msg: "Hello React"
})
}
increment() {
this.setState({
counter: this.state.counter + 1
})
}
render() {
console.log("App render ~")
const { msg, counter } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
<h2>{msg} - {counter}</h2>
<button onClick={e => this.changeMsg()}>修改msg</button>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button>
<Home />
<Recommend />
<Profile />
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export class Home extends PureComponent {
render() {
console.log("Home render ~")
return (
<div>Home</div>
)
}
}
export default Home
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import React, { memo } from 'react'
const Profile = memo(() => {
console.log("Profile render ~")
return (
<div>Profile</div>
)
})
export default Profile
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export class Recommend extends PureComponent {
render() {
console.log("Recommend render ~")
return (
<div>Recommend</div>
)
}
}
export default Recommend
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import ReactDom from "react-dom/client"
import App from "./11_render函数的优化/App"
const root = ReactDom.createRoot(document.getElementById("root"))
root.render(<App />)
|

3. 数据不可变的力量
参考:
• 我们通常写的类组件或者函数式组件都继承自 PureComponent 或者被 memo 所包裹,这样在 setState 或者 useState 的时候,都需要保证新对象和旧对象的内存地址不一样,才可以触发页面渲染。
👨🏻💻 code case:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export class App extends PureComponent {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
books: [
{
name: "计算机网络入门",
price: 23,
count: 10,
},
{
name: "你不知道的javascript",
price: 67,
count: 7,
},
{
name: "算法图解",
price: 48,
count: 3,
}
]
}
}
addBook() {
var newBook = {
name: "Golang高级程序语言设计",
price: 48,
count: 3,
}
const books = [...this.state.books, newBook]
this.setState({
books: books
})
}
render() {
const { books } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App Books</div>
<ul>
{
books.map((item, index) => {
return (
<li key={index}>name: {item.name} price: {item.price} count: {item.count}</li>
)
})
}
</ul>
<button onClick={e => {this.addBook()}}>添加一本书</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
case: 修改books的count
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export class App extends PureComponent {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
books: [
{
name: "计算机网络入门",
price: 23,
count: 10,
},
{
name: "你不知道的javascript",
price: 67,
count: 7,
},
{
name: "算法图解",
price: 48,
count: 3,
}
]
}
}
addBook() {
var newBook = {
name: "Golang高级程序语言设计",
price: 48,
count: 3,
}
const books = [...this.state.books, newBook]
this.setState({
books: books
})
}
addCount(index) {
const books = [...this.state.books]
books[index].count++
this.setState({ books: books })
}
render() {
const { books } = this.state
return (
<>
<div>App Books</div>
<ul>
{
books.map((item, index) => {
return (
<li key={index}>
name: {item.name} price: {item.price} count: {item.count} <button onClick={e => { this.addCount(index) }}> +1 </button>
</li>
)
})
}
</ul>
<button onClick={e => {this.addBook()}}>添加一本书</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
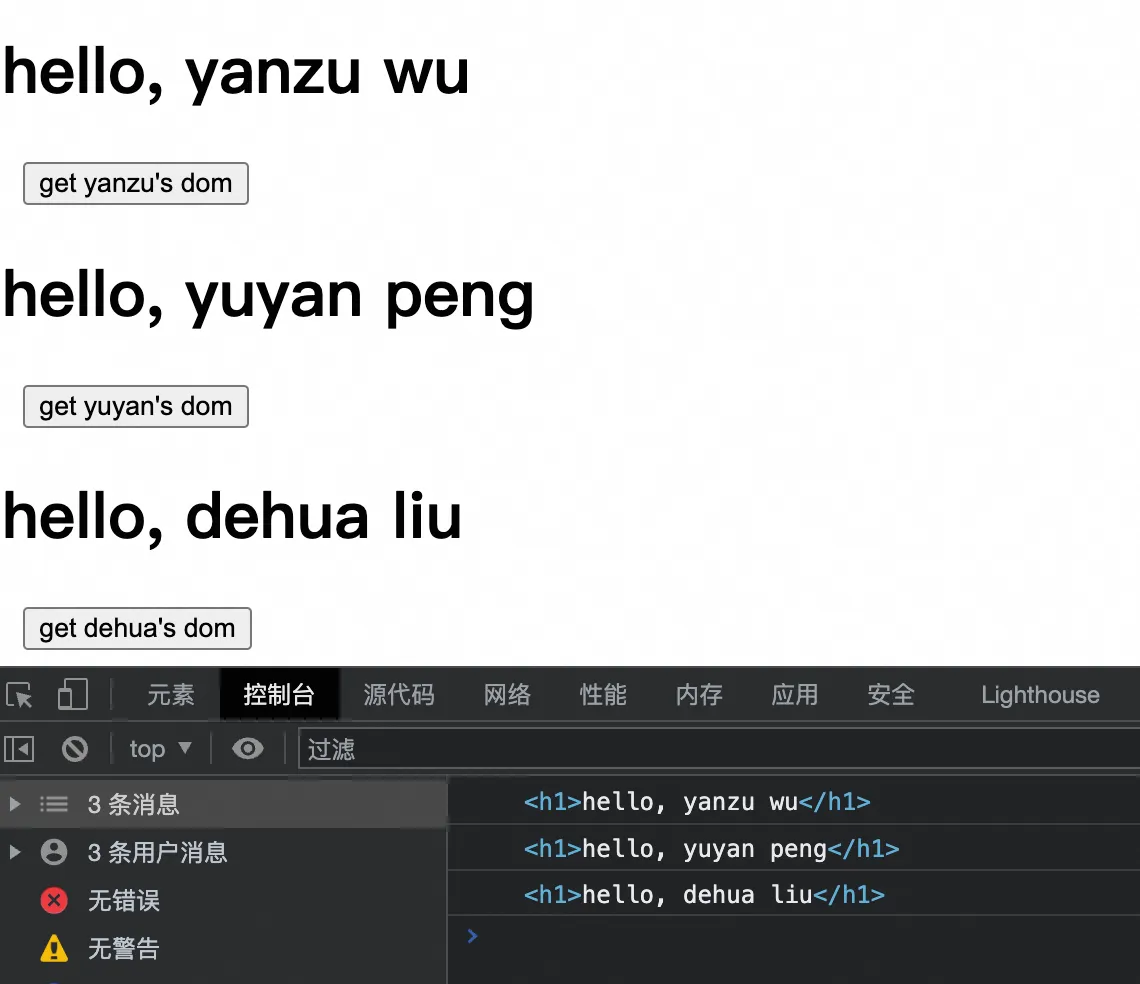
12. ref 获取原生 dom 的三种方式
• React 可以使用 ref 来获取原生 dom 对象
👨🏻💻 code case:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| import React, { createRef, PureComponent } from 'react'
export class App extends PureComponent {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = ({
})
this.yuyanRef = createRef()
this.dehuaRef = null
}
getYanzuDom() {
console.log(this.refs.yanzuRef)
}
getYuyanDom() {
console.log(this.yuyanRef.current)
}
getDehuaDom() {
console.log(this.dehuaRef)
}
render() {
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
<h1 ref="yanzuRef">hello, yanzu wu</h1> <button onClick={e => this.getYanzuDom()}>get yanzu's dom</button>
<h1 ref={this.yuyanRef}>hello, yuyan peng</h1> <button onClick={e => this.getYuyanDom()}>get yuyan's dom</button>
<h1 ref={element => this.dehuaRef = element}>hello, dehua liu</h1> <button onClick={e => this.getDehuaDom()}>get dehua's dom</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
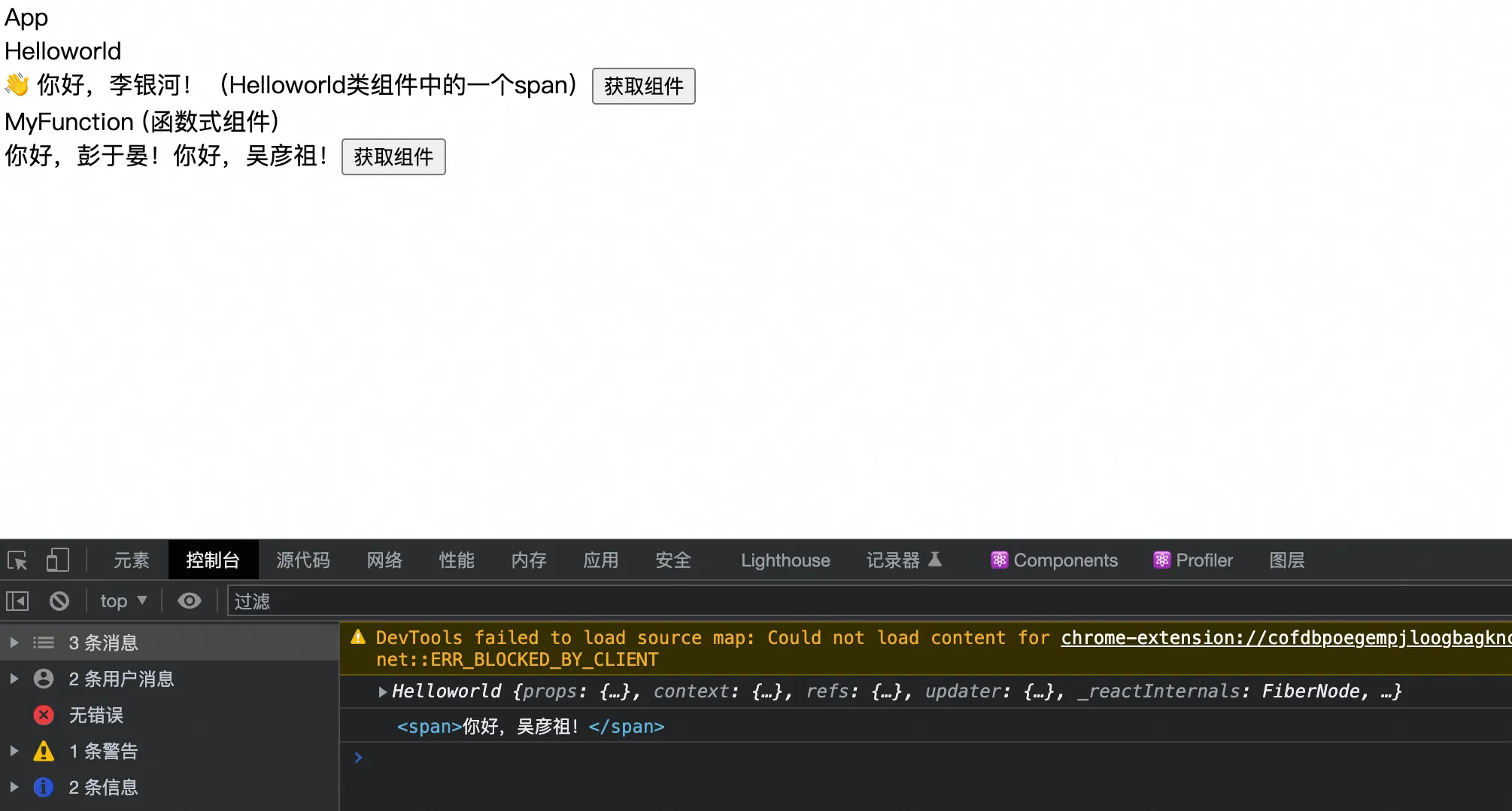
13. ref 获取组件(类组件和函数式组件)
- 通过 ref 获取组件信息,可以通过下面代码查看具体获取方式,注意函数式组件 forwardRef 和 memo 包裹函数的顺序。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| import React, { PureComponent, createRef } from 'react'
import Helloworld from './components/Helloworld'
import MyFunction from './components/MyFunction'
export class App extends PureComponent {
constructor() {
super()
this.helloworldRef = createRef()
this.yanzuRef = createRef()
}
getHelloworldRef() {
console.log(this.helloworldRef.current)
}
getYanzuRef() {
console.log(this.yanzuRef.current)
}
render() {
return (
<>
<div>App</div>
{/* 类组件 */}
<Helloworld ref={this.helloworldRef} />
<button onClick={e => this.getHelloworldRef()}>获取组件</button>
{/* 函数式组件 */}
<MyFunction ref={this.yanzuRef}/>
<button onClick={e => this.getYanzuRef()}>获取组件</button>
</>
)
}
}
export default App
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export class Helloworld extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<>
<div>Helloworld</div>
<span>👋 你好,李银河!(Helloworld类组件中的一个span)</span>
</>
)
}
}
export default Helloworld
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import React, { memo, forwardRef } from 'react'
const MyFunction = memo(forwardRef((props, ref) => {
return (
<>
<div>MyFunction (函数式组件)</div>
<span>你好,彭于晏!</span>
<span ref={ref}>你好,吴彦祖!</span>
</>
)
}))
export default MyFunction
|
14. 受控组件和非受控组件
todo
































































